How Protein Enzymes Affect Chemical Reactions
The sequence and the type of amino acid. Thats why this group of proteins has.

Enzyme Races Computer Simulation Enzymes Chemical Reactions Computer Simulation
Catalysts are molecules which affect the rate of a chemical reaction normally by speeding them up without being changed in the process.

How protein enzymes affect chemical reactions. Most enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts for chemical reactions in living systems. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by first binding to molecules and then lining them up in ways that increase the probability of the molecules exchanging atoms when they collide. Free VCE Biology notes on enzymes.
Some enzymes help break large molecules into smaller pieces that are more easily absorbed by the body. In order for most of the chemical reactions which take place in living things to occur they need a catalyst. This is different in each protein.
Enzymes are large globular proteins that reduce the activation energy required to initiate a reaction as they weaken the bonds in the substrate. Some enzymes help to break down large nutrient molecules such as proteins fats and carbohydrates into smaller molecules. How do protein enzymes catalyze chemical reactions in our bodies.
The Amoeba Sisters explain enzymes and how they interact with their substrates. Enzymes therefore allow scientists to control the exchange of atoms mechanically as explained by Science Daily. Enzymes Cells Biology FuseSchoolEnzymes are really important proteins that speed up the rates of reactions such as in photosynthesis respiration and.
This process occurs during the digestion of foodstuffs in the stomach and intestines of animals. Factors the affect the shape of the protein include the type and placement of amino acids in the chain and the envoirnement the protein is in. The present review focuses on gluten proteins and endogenous wheat components enzymes and co-factors that affect the protein network during breadmaking.
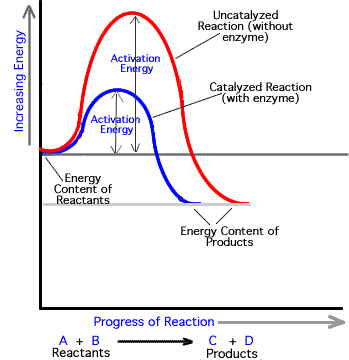
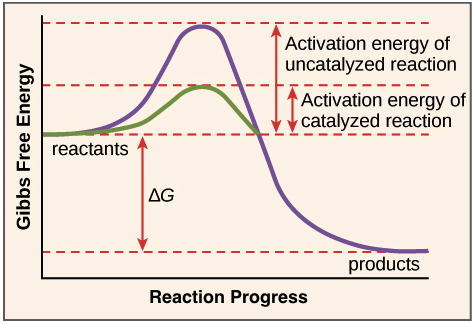
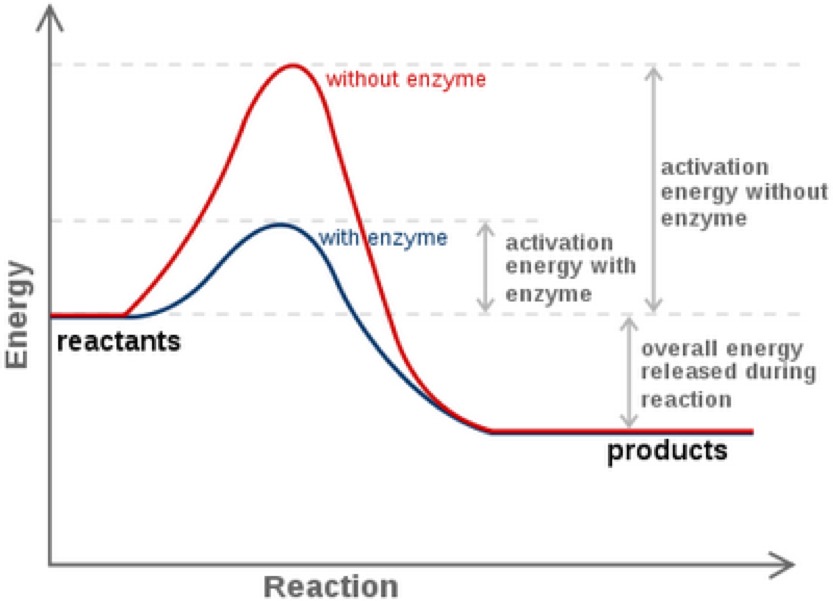
Other enzymes help bind two molecules together to produce a new molecule. Many enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Therefore they act as organic catalysts by increasing the rate of chemical reactions.
Many enzymes require a nonprotein cofactor to assist them in their reaction. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymescatalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Since gelatin contains a network of protein molecules the preparation of a gelatin fruit salad offers the opportunity to observe the action of a protease.
A catalyst is a chemical involved in but not changed by a chemical reaction. Enzymes and Chemical reactions. Catalysts play a task in accelerating chemical reactions without taking part in the reaction.
Vocabulary covered includes active site induced fit coenzyme and cofactor. In the absence of enzymatic catalysis most biochemical reactions are so slow that they would not occur under the mild conditions of temperature. The effects of exogenous components on breadmaking are reviewed by Joye et al.
By bringing the reactants closer together chemical bonds may be weakened and reactions will proceed faster than without the catalyst. How would the changing of an enzymes shape affect. The molecules upon which enzymes may affect are called substrates and also the enzyme transforms the substrates into several molecules called products.
The liver alone contains over 1000 enzyme systems. The other type of proteins fibrous proteins have long thin structures and are found in tissues like muscle and hair. Catalysts work by lowering a reactions activation energy.
Hemoglobin and Sickle cell disease Abnormal Hemoglobin in red blood cells attach to one another to turn the normally circular cell into a sickle shape it bad at carrying oxygen and is an inherited trait. Enzymes function as organic catalysts. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction.
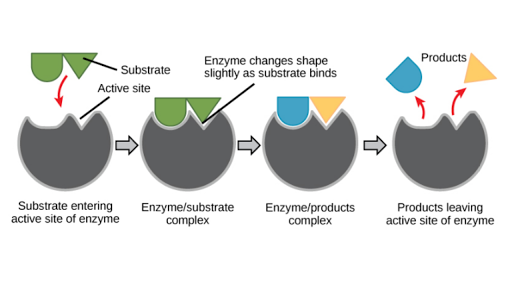
In this case the protein portion of the enzyme called an apoenzyme combines with the cofactor to form the whole enzyme or haloenzyme Some cofactors are ions such as Ca Mg and K. Their function primarily depends on the presence of an active site or substrate binding site which is a region that has a. The chemical reactions result in a new product or molecule that then separates from the enzyme.
Enzymes Enzymes are characterized as proteins functioning as biological catalysts. Enzymes An enzyme is a protein that acts as biological catalyst. Enzymes are specific and will use only particular substrates that fit into their active site similar to the way a lock can be opened only with a specific key.
Compare the activation energy with and without the enzyme. 2009 and Goesaert et al. Other cofactors are organic molecules called coenzymes which serve as carriers for chemical groups or electrons.
Enzymes are the catalysts of life and are made of proteins. An enzyme may be a globular protein that is. Enzymes are mainly globular proteins - protein molecules where the tertiary structure has given the molecule a generally rounded ball shape although perhaps a very squashed ball in some cases.
Enzymes are protein molecules that are made up of long chains of. Gluten and non-gluten proteins. The shape of an enzyme is very important to its.
Accordingly how do enzymes affect chemical reactions. Like all catalysts enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of chemical reactionsActivation energy is the energy needed to start a chemical reactionThe enzyme speeds up the reaction by lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction to start. Enzymes n z a m z are proteins that act as biological catalysts biocatalysts.
Protein - Protein - Role of enzymes in metabolism. Catalysts accelerate chemical reactionsThe molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as productsAlmost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. On average more than 100 chemical reactions occur in cells every single second and most of them require enzymes.
In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction the reactants are known as substratesSubstrates bind to a part of an enzyme called the active site and remain bound to the enzyme until the reaction is complete. Other enzymes guide the smaller broken-down molecules through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream. Although RNAs are capable of catalyzing some reactions most biological reactions are catalyzed by proteins.

Rate Of Reaction Enzymes Role Importance Expii

Enzymes Speed Up Reactions It S Not That Reactions Do Not Occur Without Enzymes But They Certainly Make Th Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Science Biology

Enzyme Lab Enzymes Biology Chemical Reactions Enzymes

Http Iws Collin Edu Biopage Faculty Mcculloch 1406 Outlines Chapter 206 Ra74 Jpg Chemical Reactions Higher Education Energy Supply

Factors Affecting Enzyme Action Biologia Tema Bachillerato

Effect Of Enzyme Concentration On Reaction Rate Reaction Rate Enzyme Kinetics Enzymes

Enzymes Biology For Non Majors I

Pin On Https Drawittoknowit Com
How Do Enzymes Speed Up The Chemical Reactions Use Activation Energy In Your Answer Socratic

Catalyst Speeds Up A Chemical Reaction By Lowering The Activation Energy Ea Of The Overall Reaction It Will Not Affect Quimica Quimica Organica Termodinamica
Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy
Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy

Enzyme Rate Of Reaction Factors Catalysts Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Enzymes Overview Enzymes Reactions Biology
How Enzymes Speed Up The Chemical Reactions Ck 12 Foundation



Posting Komentar untuk "How Protein Enzymes Affect Chemical Reactions"