How Do Enzymes React To Heat
Enzymes work best within specific temperature and pH ranges and sub-optimal conditions can cause an enzyme to lose its ability to bind to a substrate. The same effect can be obtained by physically stirring the ingredients.
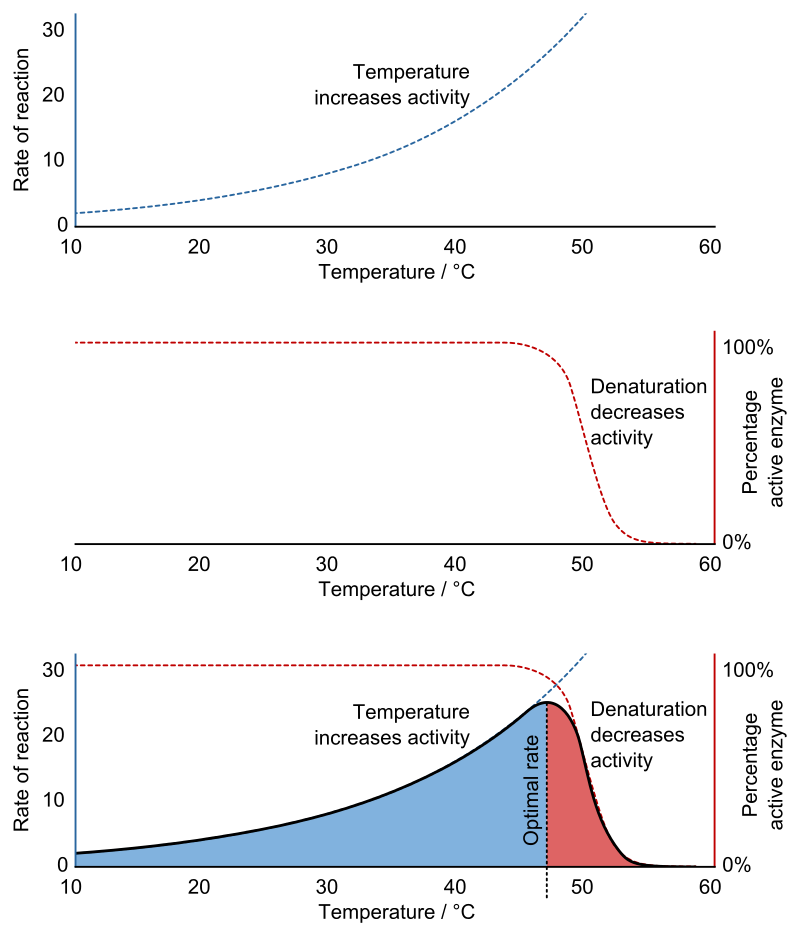
9 8 The Effect Of Temperature On Enzyme Kinetics Chemistry Libretexts
Some examples of enzymes and their specific substrates.
How do enzymes react to heat. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on. Not only does heat change the shape of an enzyme it changes its pH level as well causing the enzyme to stop working. Although enzymes are changed by heat they cannot be killed because they are not living things.
One common source of structural change is heat. Enzyme names and classification. Warm temperatures tend to enhanced enzymatic activity by increasing the kinetic energy associated with random molecular motion but when the temperature becomes excessive enzymes experience structural deterioration that inhibits enzymatic activity.
A ten degree Centigrade rise in temperature will increase the activity of most enzymes by 50 to 100. The permanent change comes from heat changing the shape of the enzyme which stops it from working properly. Any change in this pH significantly affects the enzyme activity andor the rate of reaction.
Oxidase dehydrogenase carboxylase although individual proteolytic enzymes generally have the suffix -in eg. Competitive Inhibitors Enzyme activity can be stopped by. Enzymes as biological catalysts activation energy the active site and environmental effects on enzyme activity.
In general the rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are faster as temperature increases and slower as temperatures decrease below an optimal temperature level. Enzymes as biological catalysts activation energy the active site and environmental effects on enzyme activity. Often the trivial name also indicates the substrate on which the enzyme.
To know more about the relation between pH and enzymes andor the effect of pH on enzymes. Almost all of the over 2000 known enzymes are proteins nearly all of which operate with cofactors metal ions or organic molecules coenzymes. Enzymes typically have common names often called trivial names which refer to the reaction that they catalyse with the suffix -ase eg.
When temperature increases more molecules have more kinetic energy to react so reaction speed increases. Temperature At low temperatures the number of successful collisions between the enzyme and substrate is reduced because their molecular movement decreases. Brought to you by Sciencing.
The reason for this is because once the enzyme performs its duty it is free to do more work. Enzymes actually lower the energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur. Enzymes because of their chemical specificity provide a matrix where chemical reactions can occur.
The matrix allows the chemical reaction to occur at a much lower energy level. Like most chemical reactions the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction increases as the temperature is raised. The human body is.
This alters the shape of the active site so that substrates cannot bind to it the. Basically enzymes reduce the activation energy needed to start a reaction by temporarily bonding with the reacting molecules and in so doing weakening the chemical bonds. The reaction is slow.
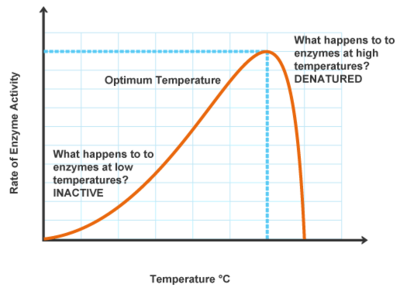
Raising temperature generally speeds up a reaction and lowering temperature slows down a reaction. Enzymes work fastest when they are at the optimum temperature but as the temperature gets lower the enzymes activity begins to decrease. Variations in reaction temperature as small as 1 or 2.
There are many reactions that would not occur at all without the functioning of enzymes. If the temperature is too high or if the environment is too acidic or alkaline the enzyme changes shape. For instance animals from the Arctic have enzymes adapted to have lower optimum temperatures while animals in desert climates have enzymes adapted to higher temperatures.
The rate determining step for an enzyme-substrate reaction is always the second step in which ES is converted into the product. There are several factors that can increase the rate of a reaction. Raising the temperature can speed a reaction because the molecules have more energy and therefore bump into each other more frequently.
Once an enzyme can do more work after conversion a reaction can go faster. For every enzyme there is an optimum pH value at which the specific enzyme functions most actively. While higher temperatures do increase the activity of enzymes and the rate of reactions enzymes are still proteins and as with all proteins temperatures above 104 degrees Fahrenheit 40 degrees Celsius.
Enzymes are proteins that all organisms use to cause chemical changes MedLinePlus explains 1One of the interesting things about enzymes is that although they can cause a permanent change in the chemical structure of a substance the enzymes themselves do not change which means that one enzyme molecule can be used repeatedly.

Temperature Enzyme Reaction Rates Effects Examples Expii
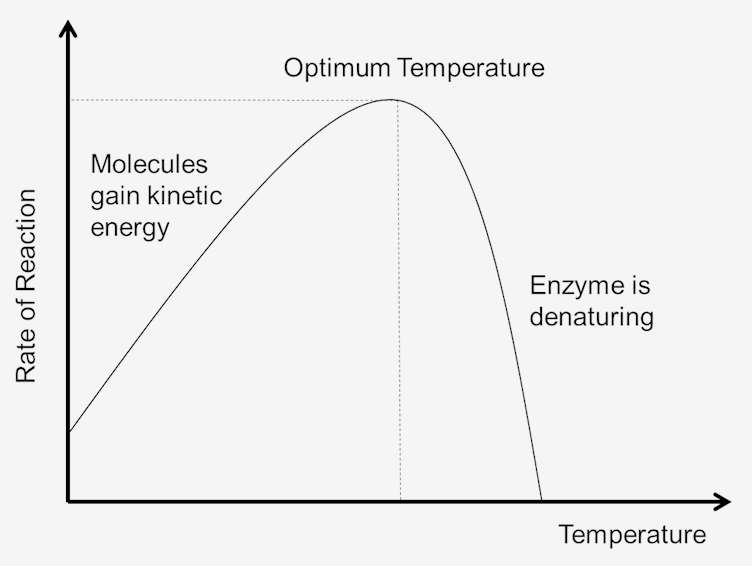
Effect Of Temperature On Enzymatic Reaction Creative Enzymes
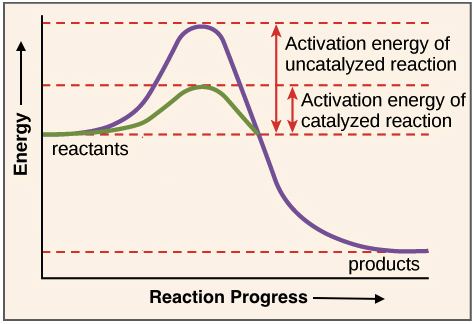
Enzymes Review Article Enzymes Khan Academy

Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity A Level Notes
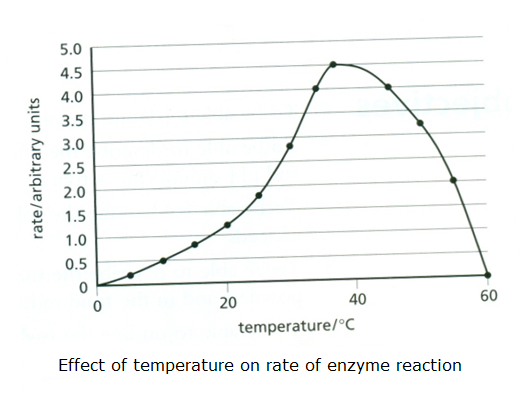
Enzymes And Reactions Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
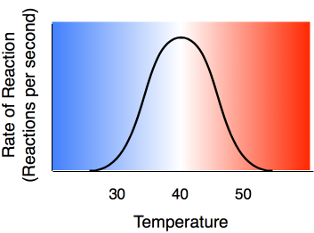
5 5 Temperature Ph And Enzyme Concentration On The Rate Of A Reaction Chemistry Libretexts
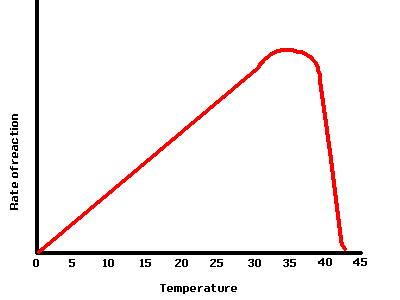
Gcse Biology How Temperature Effects Enzymes
Biochemistry Enzymes Temperature Pathwayz

Effect Temperature On Enzyme Activity Enzymes Activity Biochemistry Enzymes

Temperature Enzyme Reaction Rates Effects Examples Expii
Johnson Matthey Catalysts Education Enzymes
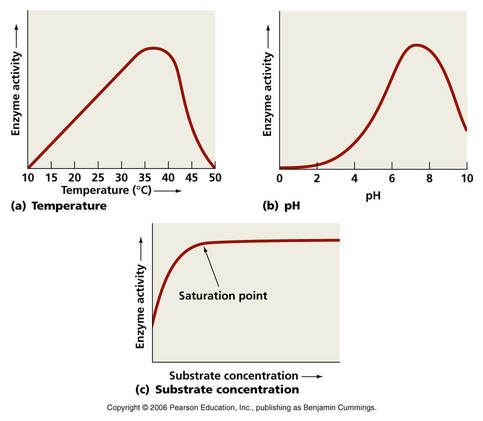
Topic 2 5 Enzymes Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Temperature Enzyme Reaction Rates Effects Examples Expii
Effect Of Temperature On Enzyme Action Brilliant Biology Student
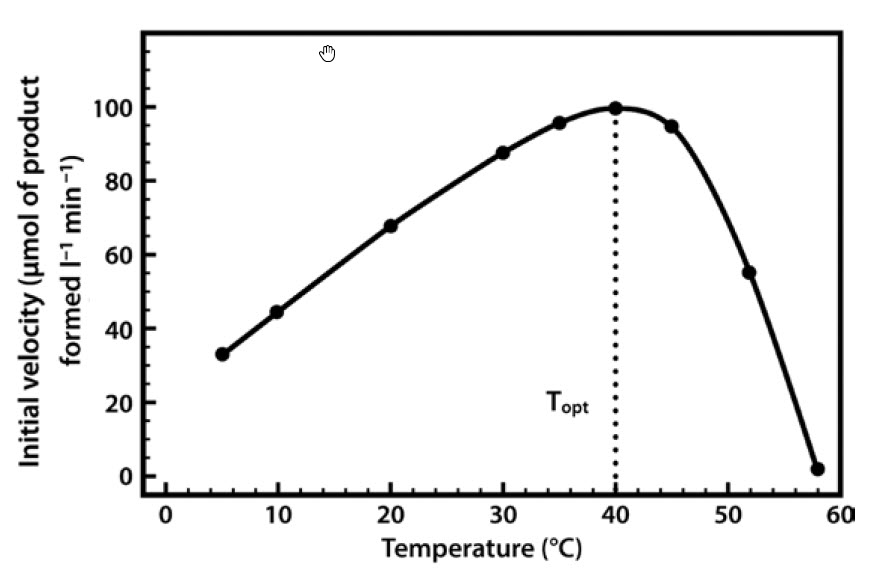
Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry




Posting Komentar untuk "How Do Enzymes React To Heat"