How Does Xylem And Phloem Move
Xylem and Phloem Xylem and Phloem are two different types of vascular tissues which are mainly involved in the transportation process. These substances move up the plant from the roots to leaves.
Difference Between Xylem And Phloem Major Differences
The mechanism of phloem transport remains unclear see below.

How does xylem and phloem move. In principle either xylem or phloem could provide the plumbing through which water moves up a tree trunk or other stem. - In a leaf xylem and phloem make up a network of veins which support the thin leaves. Since grade school weve learned that the xylem or wood transports water from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant while the phloem transports sugars and other organic materials.
The term xylem is derived from the Greek word xylon meaning wood. Xylem is just an array of emptied dead cells with no inherent directional structure. 2 the hydrostatic pressure at the top of the xylem vessel becomes lower than the pressure at the bottom 3 this pressure difference causes water to move up the xylem vessels in continuous columns as the higher pressure at the bottom pushes water up the vessel.
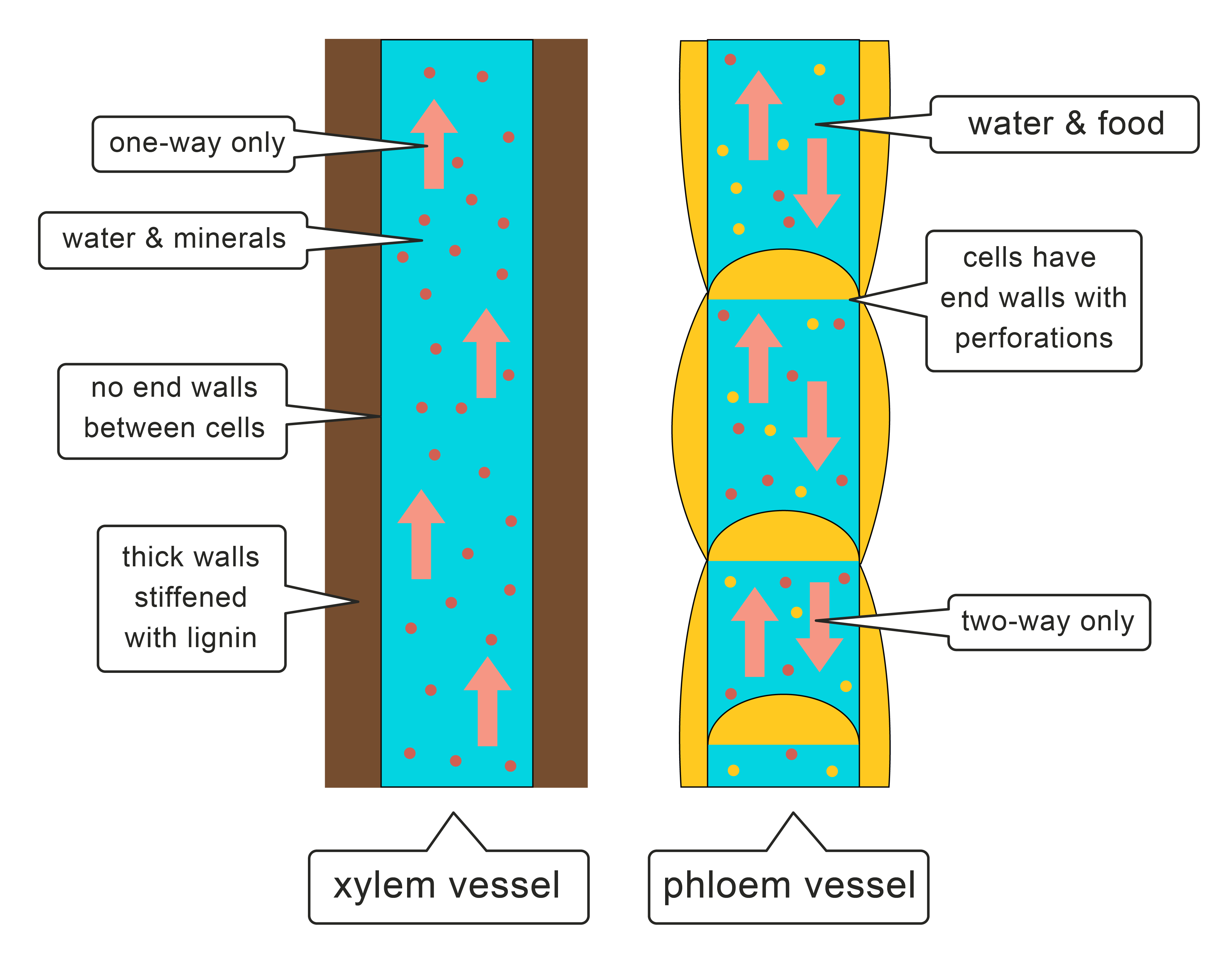
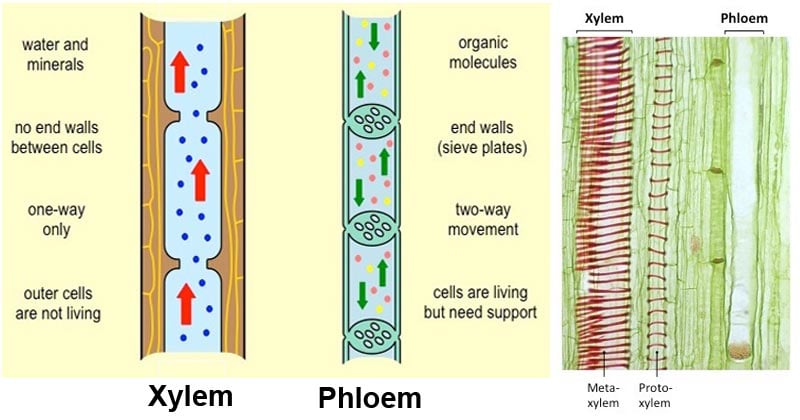
Xylem and phloem are the two types of vascular tissues in vascular plants. This type of tissue consists of living cells that are separated by end walls with tiny perforations or holes. During transpiration water evaporates from the leaves and draws water from the roots.
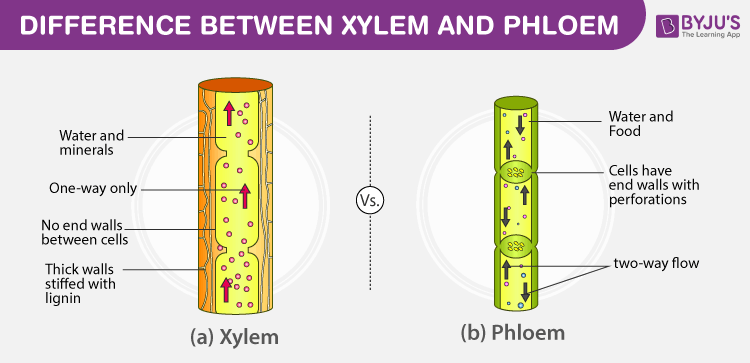
Phloem is vascular tissue that transports food sugar dissolved in water from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth or storage. Xylem tissue transports water and mineral ions in solution. Transportation is a process of transporting water minerals and food to all parts of the plant body.
- In a root the xylem is in the centre surrounded by phloem to provide support for the root as it pushes through the soil. It willwould pass fluid equally well in either direction. Vascular plants are able to grow higher than other plants due to the rigidity of xylem cells which support the plant.
Phloem is responsible for transporting food produced from photosynthesis from leaves to non-photosynthesizing parts of a. These tissues form a vascular bundle and these work together as a unit. Glucose made in photosynthesis is then moved to all cells in phloem vessels for.
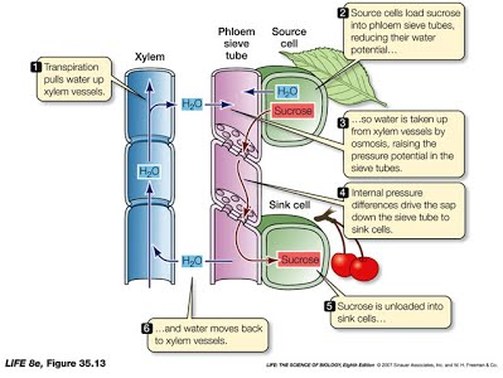
Xylem and phloem will play an important role in Transpor. Xylem and phloem in stems Xylem and phloem travel entire length of stems in discrete threads called vascular bundles. This movement of water into the sieve tube cells cause p to increase increasing both the turgor pressure in the phloem and the total water potential in the phloem at the source.
In general however water movement in the xylem is by transpiration pull. The xylem and the phloem make up the vascular tissue of a plant and transports water sugars and other important substances around a plant. The xylem moves water and solutes from th.
As you have learned earlier these two vessel systems are called xylem and phloem. Phloem is responsible for transporting sugars proteins and other organic molecules in plants. What does phloem tissue transport Phloem tissue mainly transports sugars also in solution both up and down the plant.
Likewise phloem is also just a series of tubes but live ones that are sustained by an adjacent cell. - In the stems the xylem and phloem are near the outside to provide a sort of scaffolding that reduces bending. Though true this has resulted in the notion that sucros.
In eudicots vascular bundles are arranged in a ring within the stem. Xylem transports and stores water and water-soluble nutrients in vascular plants. Which is itAn elegant experiment demonstrates which of.
Xylem and Phloem - Transport in Plants Biology FuseSchoolPlants have a transport system to move things around. During transpiration plants move water from the roots to their leaves for photosynthesis in xylem vessels. Xylem moves water from roots to the leaves and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
The movement of xylem is unidirectional while. Phloem on the other hand is the living permanent tissue that carries food and other organic nutrients from leaves to all other parts of the plant. It can and does pass fluids in either direction.
The presence of high concentrations of sugar in the sieve tube elements drastically reduces s which causes water to move by osmosis from xylem into the phloem cells. Each vascular bundle is orientated with the xylem on the interior and the phloem on the outside of the xylem. Movement in the xylem is by mass flow of the whole solution and the force is either the tension pull of transpiration or root pressure or both.
Xylem is the dead permanent tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to all other parts of the plant.
Topic 9 2 Transport In The Phloem Of Plants Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Sugar Transport In Plants Phloem Organismal Biology
File Flow And Exchange Of Nutrients In The Phloem And Xylem Of Plants Svg Wikimedia Commons
How Do Xylem And Phloem Cells Differ Quora

Xylem Phloem Communication Network Control Over Nitrogen Fixation In Download Scientific Diagram

Photosynthates Biology For Majors Ii
Which Part Of A Plant Are Xylem And Phloem Found In Quora

Xylem And Phloem A Level The Science Hive

Transport Pathways Of Nutrients And Water By Xylem And Phloem In A Download Scientific Diagram

Plant Transportation A Closer Look At Xylem And
Transport Of Water And Solutes In Plants Choral Explanation Examples

25 4b Vascular Tissue Xylem And Phloem Biology Libretexts
Understand The Roles Of Xylem And Phloem In Plants Worksheet Edplace

Phloem Vs Xylem Difference And Comparison Diffen Biology Plants Biology Plant Science


Posting Komentar untuk "How Does Xylem And Phloem Move"